Share this
Battery Internal Ohmic Measurements Explained - Part 1 (Impedance)
by PowerShield on Oct 18, 2019 1:21:32 PM
Introduction
Once an internal ohmic measurement has been taken on a battery, the next questions are:
- What does it mean?
- Can it be compared to a reading taken with another device?
- Can the reading be influenced?
In a series of articles, we will delve into answering these questions and many more related items associated with the measurement.
The IEEE 1881 definition of internal ohmic measurement is: “A measurement of the electronic and ionic conduction paths within a cell or unit, expressed in terms of impedance, resistance, conductance or admittance.”
This term was created by IEEE so that the industry can use one term. This was the result of several manufacturers in the 1990s campaigning on a specific term and associating it with their equipment.
In the following series I will use the electrical term impedance as this, in my opinion, is the appropriate scientific term to use.
Why is battery impedance measurement useful?
For VRLA batteries and some other chemistries, this measurement can detect battery failures and determine the end of life for a battery by trending the measurement without the need for a discharge test.
Below is the battery impedance over the life of a VRLA battery.
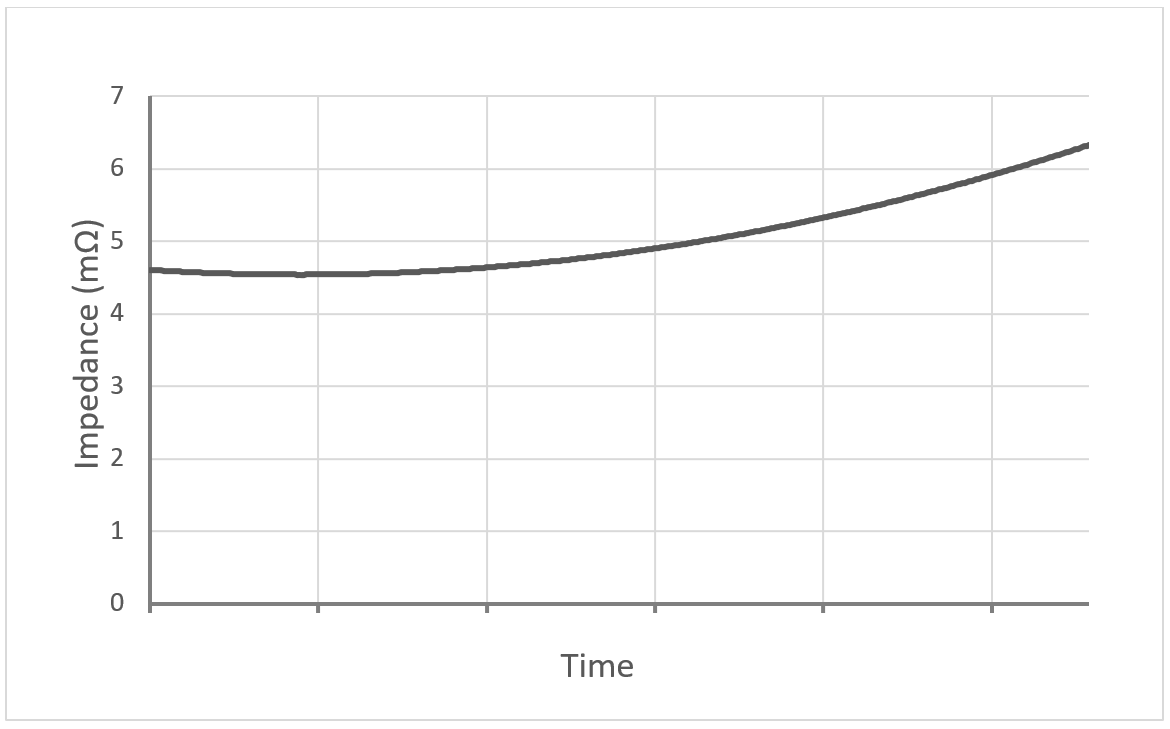
By extrapolating the battery impedance history, the end of life can be determined, meaning the battery replacement can be planned instead of using a calendar-based approach.
By observing the rate of impedance change in the batteries, faulty units can be identified. Below is the impedance history for several strings of batteries for a UPS installation.
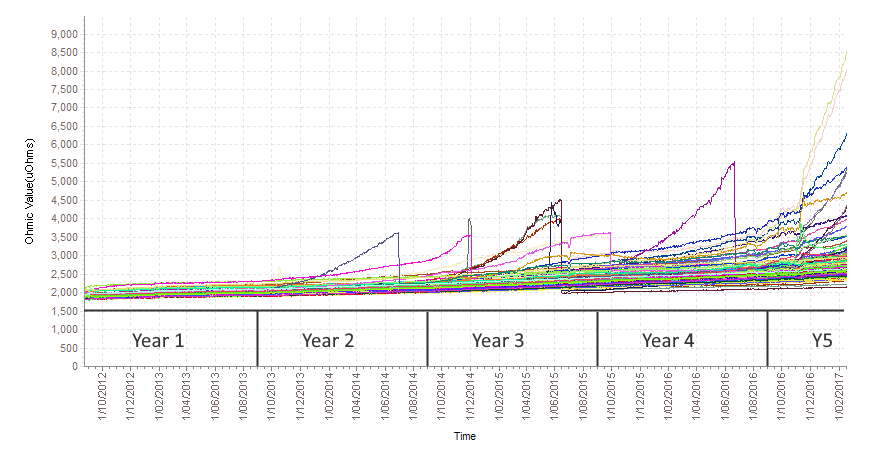
The batteries with a higher impedance rate of change and a higher impedance are failures. You can easily see when the failures are replaced from the vertical lines in the graph.
How can you measure the impedance of a battery?
To take a battery impedance measurement a change in voltage has to occur. The battery impedance is dependent on the rate of change (frequency) and amplitude of the test signal applied to the battery.
To cause a change on the battery, depending on the equipment used the test signal may draw out energy, inject energy or both. For permanent battery monitoring equipment, the typical method is for the test signal to draw out a small amount of energy from the battery under test.
What is battery impedance?
Battery impedance is the electrical resistance and the ionic resistance.
Challenges
In order to interpret a battery impedance reading, a certain level of knowledge is required to ensure that the measurement is used correctly. There are a number of factors that can influence a reading, including:
- There is no industry standard specifying the method for taking a battery impedance measurement, e.g., test signal amplitude or test signal frequency. Therefore, each device manufacturer is using their own recipe. The battery is not a simple resistor, hence the need to measure impedance. Different recipes will produce different readings for the same battery.
- Impedance of a battery is typically very low, so it is easy to introduce error by the location of the test probes or test points, e.g., different probe locations when taking readings with a handheld instrument.
- When the measurement is taken online, in-circuit influences can affect the measurement:
- Parallel batteries
- Changes in the load or charger for small strings i.e., two 12V battery string for a generator.
- Ripple or interference from rectifiers, inverters, loads, and other sources. A reading may be obtained but it will have poor repeatability due to the high level of ripple. This effect will not show until a number of readings are taken on the same battery.
- Temperature and battery state of charge.
- Number of batteries tested with a single measurement.
- Test point location on a multi-post battery
The key points when using impedance readings are:
- Repeatable consistent measurements
- Trending measurements over time
- Looking for rate of change over time
- Do not try and compare readings from different devices unless you understand all the parameters that influence a battery impedance measurement and can determine whether it is technically feasible.
The following articles will explore the detail of these influences and assist with gaining a deeper understanding of battery impedance measurement.
For further insights into the topic of impedance measurement, explore the other articles in the series:
Battery Internal Ohmic Measurements Explained – Part 2 (Kelvin Connection)
Battery Internal Ohmic Measurements Explained – Part 3 (Importance of Context)
Share this
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
Battery Internal Ohmic Measurements Explained - Part 2 (Kelvin Connection)
Battery Internal Ohmic Measurements – Part 3 (Importance of Context)
Thermal Runaway and Thermal Walkaway
- September 2024 (1)
- December 2021 (2)
- March 2020 (1)
- January 2020 (1)
- December 2019 (1)
- October 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- May 2019 (2)
- April 2019 (1)
- March 2019 (2)
- January 2019 (1)
- December 2018 (1)
- November 2018 (1)
- August 2018 (3)
- July 2018 (1)
- June 2018 (2)
- May 2018 (2)
- March 2018 (2)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (1)
- November 2017 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (3)
- June 2017 (1)
- March 2017 (1)
- November 2016 (1)
- October 2016 (1)
- September 2016 (2)